摘要
| 论文 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/2206.07389.pdf |
|---|---|
| code | https://github.com/cfzd/Ultra-Fast-Lane-Detection-v2 |
| 时间 | 22 |
| 优势 | 基于row anchor 对于垂直车道线好,基于col对于扁平的车道线好。 |
| 状态 | 待开始 阅读中 已读完 |
概论
- [x] Edit By Porter, 积水成渊,蛟龙生焉。
引言
1.相对于论文1(UFLD)解决的问题是什么,如何解决(创新点)?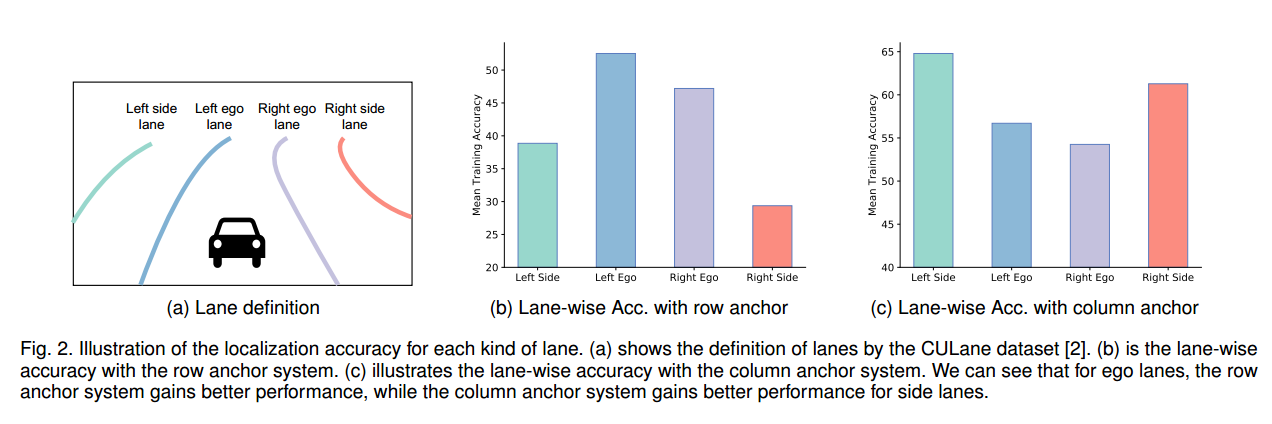
论文指出,“ Our observation is that the row anchor systems may not work well for all kinds of lanes, and it could cause a magnified localization problem. As shown in Figs. 2a and 2b, the localization accuracies for side lanes are significantly lower than those for the ego lanes when using row anchors. What if we use column anchors?”
- 基于row anchor 的车道线识别系统并非对所有车道线检测同样有效,如上图2a,2b所示,最边上的两条车道线检测精度低于中间两条车道线的检测精度(ULFDv1仅仅使用这种方法)。
- 基于col anchor 的车道线检测效果如图2c所示,可以看出基于col的车道线检测两侧边车道线识别友好,识别精度高(将结合使用的新方法)。
针对如何提高两侧车道线识别精度的解决方案,“With the above observation, we propose to use hybrid (row and column) anchors to represent different lanes separately. pecifically, we use row anchor for ego lanes and column anchor for side lanes. In this way, the magnified localization error problem can be
relieved, and the performance can be improved.” 使用混合(row and colum) 方法,解决上面问题。
2.通过混合raw和col的锚点坐标coordinate,如何来学习和定位这些coordinate是一个问题。“How to effectively learn these coordinates is another important problem. The most straightforward method is to use regression”,提高定位精度如何实现(创新点)?
- 常见的定位方法为回归的思路来做的,为了增大全局的感受野预测,提出了一种基于分类的车道线坐标(coordinate)学习方法(这个和ufldv1是一种思路),即用不同的类来表示不同的车道线坐标。“we propose to learn the coordinates of lanes in a classification-based manner, which represents different coordinates using different classes.”
- 此外,“ In this work, we further extend the original classification to the ordinal classification. In the ordinal classification, adjacent classes have close and ordinal relationships, which is different from the original classification”。将原始的分类扩充到有序分类问题,相邻车道线坐标点具有紧密的有序关系。
- 有序分类的另一个性质是类的空间是连续的,比如第二条车道线旁边是第一条或者第三条车道线。“ we propose two loss functions together to modeling the ordinal relationship between classes, including a base classification loss and a mathematical expectation loss. Utilizing the ordinal relationship and continuous class space properties, we can use the mathematical expectation instead of argmax to get the continuous class [19] of prediction.” 提出两个损失函数一起建模类间的有序关系,包括基于分类损失和数学期望损失。利用空间关系和连续类间关系,使用数学期望代替代替argmax来得到预测的连续类。
论文创新点总结
论文创新
- 工作的主要贡献有三个方面。
1)我们提出了一种新颖、简单、有效的车道检测公式。基于anchor的车道线坐标,并以基于分类的方式学习坐标。
2)在此基础上,提出了一种混合锚系统,进一步扩展了原有的raw anchor系统(相当于ufldv1的升级),可以有效地减小定位误差。
此外,将基于分类的学习进一步扩展为有序分类问题,在基于分类的定位中利用自然的有序关系。
3)该方法达到了最先进的速度和性能。我们最快的模型可以达到300+ FPS,与最先进的性能相当。
相对于第一篇论文改进点
- Hybrid Anchor System With the observation of the magnified error problem, we propose a new hybrid anchor system that could effectively reduce localization error compared with the previous publication.
- Ordinal Classification Losses We propose the new loss functions that treat lane localization as an ordinal classification problem, which further improves the performance.
- Presentation & Experiments Most of the paper is rewritten to give clearer presentations and illustrations. We provide more analyses, visualizations, and results to better cover the space of our work. Stronger results with 6.3 points of performance improvement at the same speed are also provided in this version.
相关工作(论文解读)
论文提到,自底向上的注意力机制和自上而下的注意力机制,虽然论文说了采用自上而下的注意力机制,但是这里额外介绍下两者区别。
20世纪50年代,美国著名物理学家、诺贝尔奖得主Richard P.Feynman 在题为《底部广阔的空间》(《There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom》)的著名演讲中指出将来科学家将能够安排原子排列并进行**“由下而上”的结构组成方式。在底层空间制造任何东西!如果我们对物体微小规模上的排列加以某种控制的话,我们就能使物体得到大量的异乎寻常的特性,就会看到材料性能将会产生丰富的变化。
通常来说,“自上而下”(Top-Down)的方法就一种是将较大尺寸(从微米级到厘米级)的物质通过各种刻蚀技术来制备我们所需要的纳米结构,一般统称为纳米刻印技术。
将一些简单的,较小的结构单元(如原子,分子,纳米粒子等)通过弱的相互作用自组装构成相对较大,较复杂的结构体系(在纳米尺度上),人们将这种方法称之为“自下而上”(Bottom-Up)法。自组装是一种不需要人干预的,通过各种类型的相互作用力自发的将较小的结构单元(如原子,分子,纳米粒子等)组织成各种有序图案结构的方法。
参考: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/264408975
自下而上的方法包括,常见的传统图像处理方法,使用图像底层特征,利用HSI和图像的边缘提取算法来实现车道线检测。或者使用立体视觉技术,或者激光雷达的反射光强度等思想进行车道线检测。
本文方法是自上而下的建模方法。该方法通过自顶向下的建模,自然能够更加关注全局信息**,有利于解决无视觉线索问题。与以前的自顶向下方法相比,我们的方法旨在建立一种新的车道检测公式,该公式采用行锚车道和混合锚车道表示,大大降低了学习难度,加快了检测速度。根据之前会议版本[20]提出的公式,我们的工作已被成功采用并推广到其他方法中[52]。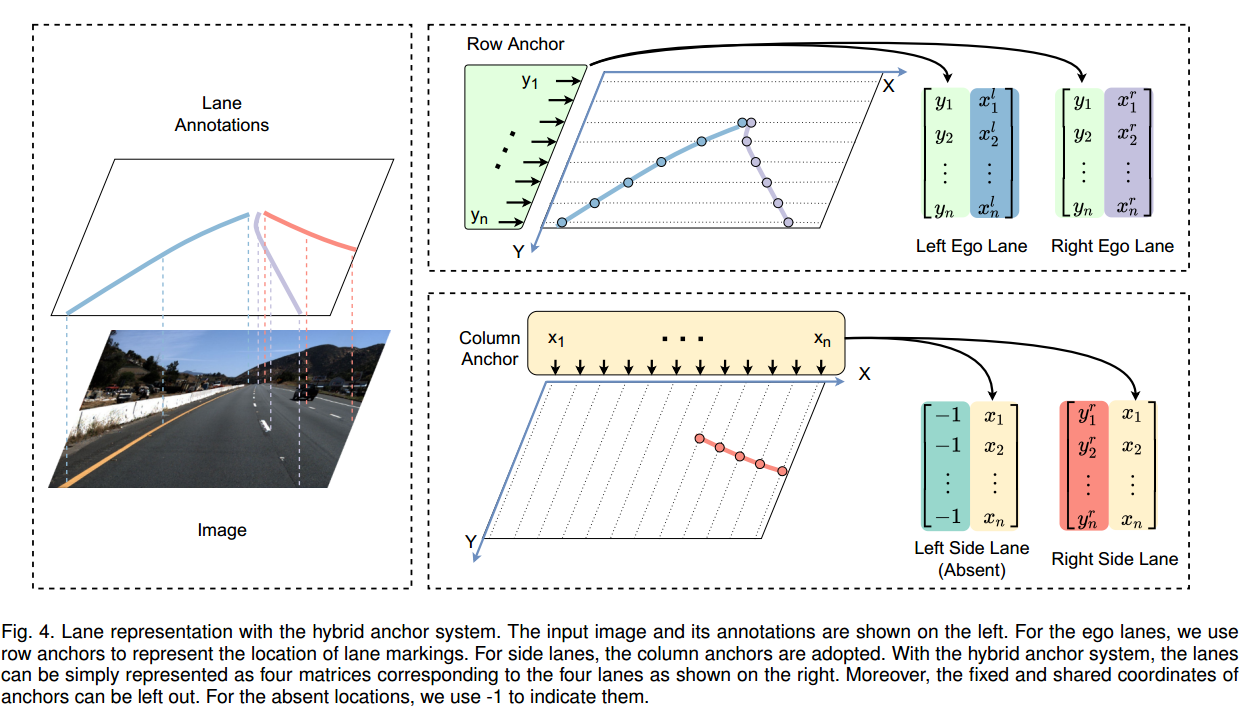
如上图,执行车道,l,r 车道,使用raw anchor, side lane ,例如rr或者ll我们采用coloumn来进行车道线检测。
在混合锚系统中,车道可以简单地表示为四个矩阵,对应于右图所示的四个车道(上图红色矩阵表示红色车道,其他颜色递推)。此外,锚点的固定坐标和共享坐标可以省略。对于不存在的位置,我们使用-1来表示它们。
在culane数据集的训练中
- 输入样本1640x590,1640宽,590高
- Raw anchor = num_row=72, row 上分为num_cell_row=200个cell, 每行200个cell
- Column anchor=num_col=81,cplumn 上分为num_cell_col=100个cell,每列100个cell
算法细节描述
基于anchor的车道线表示
暂时无法在飞书文档外展示此内容
如图所示,这里介绍了为何仅仅raw anchor 存在会导致放大误差的问题,“In order to represent lanes, we introduce the row anchors for lane detection, as shown in Fig. 3. Lanes are represented with points on the row anchors. However, the row anchor system might cause a magnified localization error problem, as shown in Fig. 2. In this way, we further extend the row anchor system to a hybrid anchor system.”如上图蓝色区域为理想的误差区域,紫色区域为放大的定位误差区域。
非混合anchor方法存在的问题,“the row anchors hard to localize the lanes which are more horizontal (typically
side lanes), and similarly, it makes the column anchors hard to localize the lanes which are more vertical (typically ego lanes). Instead, when the lanes and anchors are vertical, the error introduced by the anchor system is minimal (θ = 0 in this case), and it equals the ideal localization error.”,问题是,非混合anchor 方法很难完成水平或者垂直的车道线检测任务。
针对上面的放大定位误差问题,结合culane或者tusample数据集设置定位规则,“a lane can only be assigned with one kind of anchor, and the more vertical anchor type to the lane is chosen. ”,所以算法使用“we use row anchors for ego lanes and column anchors for side lanes, and the magnified localization error problem can be relieved by the hybrid anchor system.” row anchor 表示直行车道(r,l), column anchor 表示两边车道(rr,ll).
“ we first assign the corresponding anchor system, which has the minimal localization error. Then we calculate the line–line intersection between the lane and each anchor, and record”,首先指定最小定位误差的相应锚点系统,并记录相交的坐标。如果车道在该锚点处没有坐标,则用-1表示。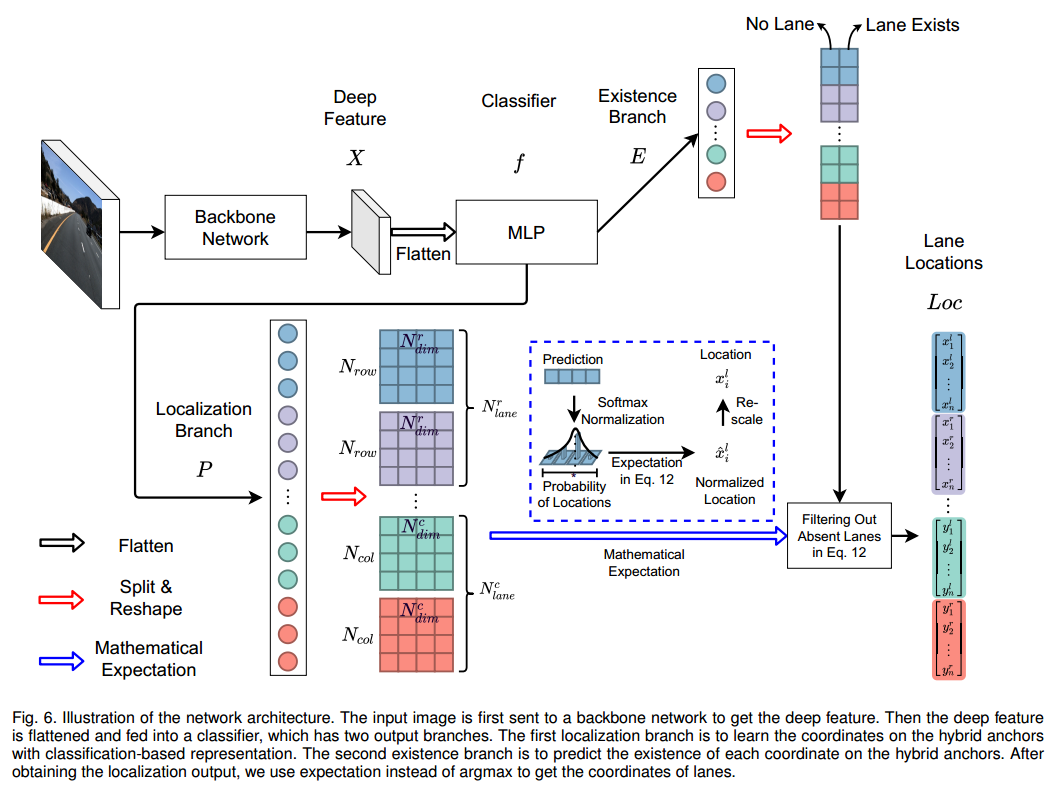
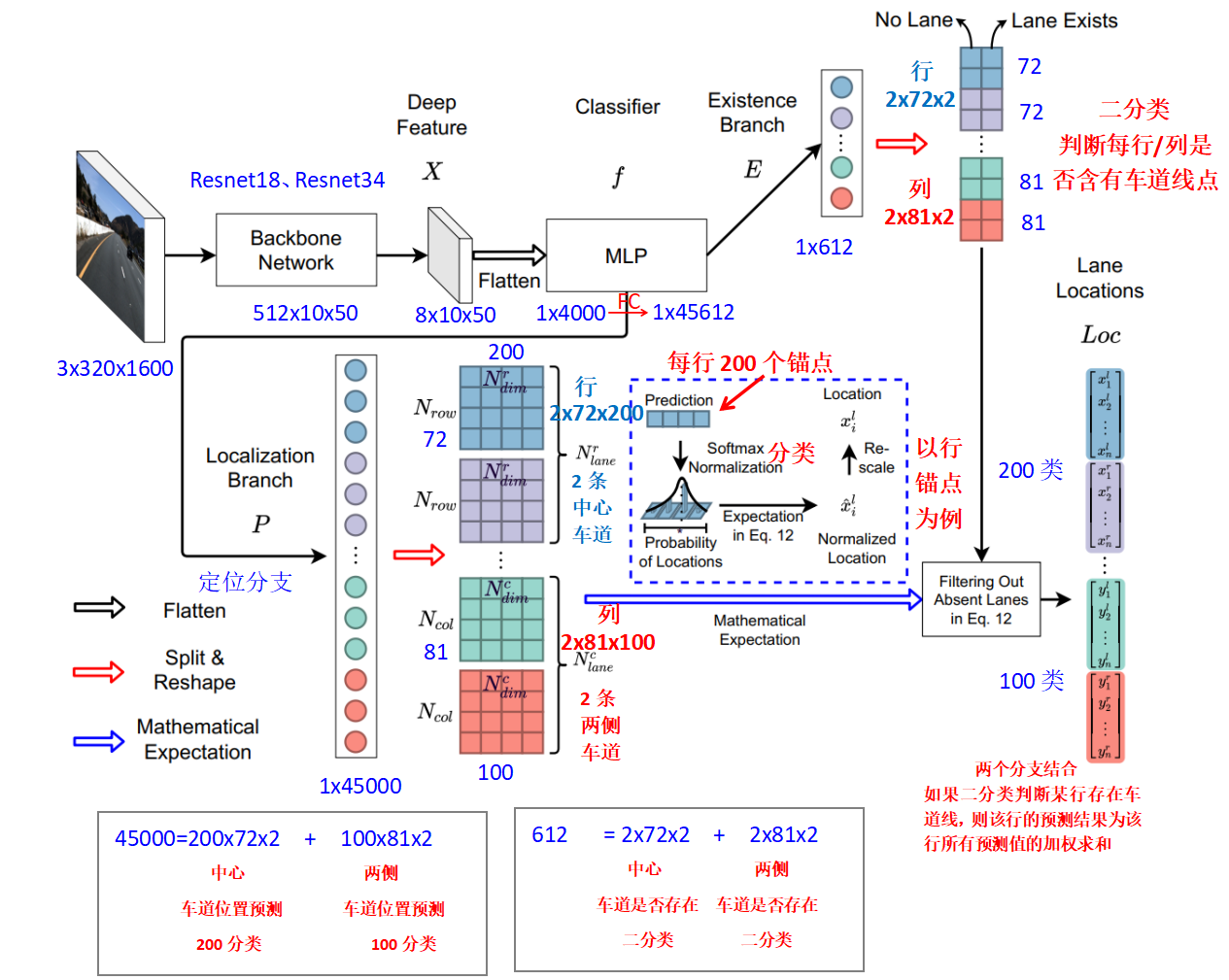
模型网路结构
模型最终输出为存在分支和定位分支。
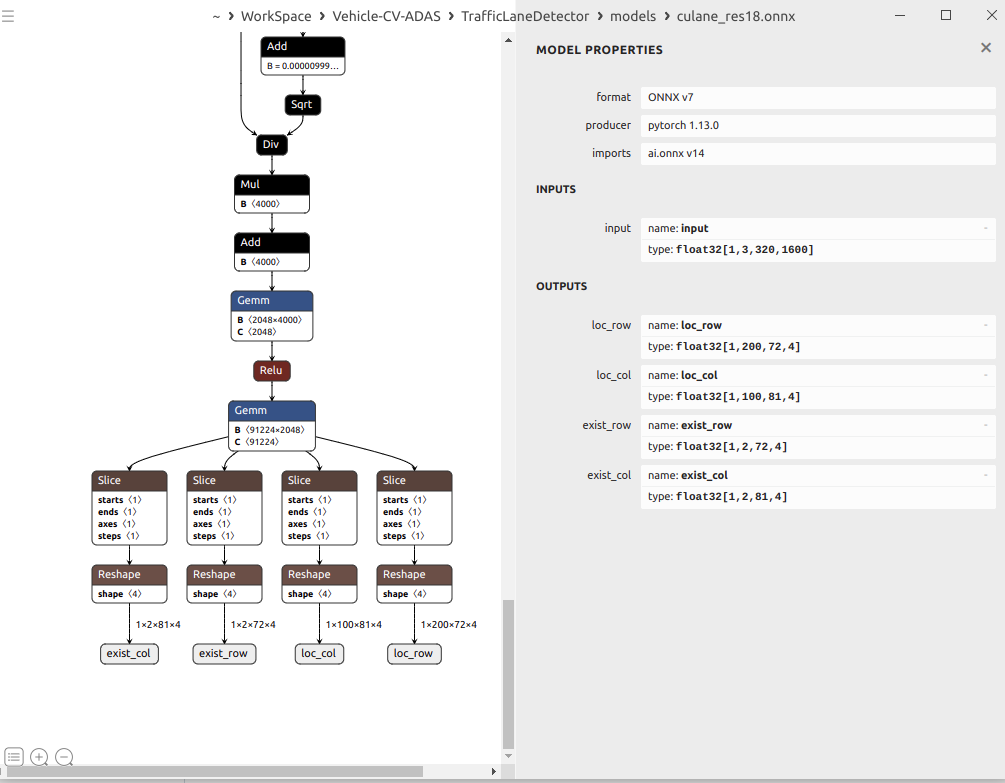
所以,模型输出的解释为
暂时无法在飞书文档外展示此内容
exist_row、exist_col:
如下图论文解释,row上使用了分类的思想,每个exist_row,存在两组[0的预测概率,1的预测概率],所以存在车道线,需要[0小,1大]。exist_col也是类似的思想。
默认参数
exist_row[1,2,72,4],其中2表示[0的概率,1的概率],存在车道线,需要1的概率大于0的概率。
exist_col[1,2,81,4],其中2表示[0的概率,1的概率],存在车道线,需要1的概率大于0的概率。
loc_row和loc_raw:
loc_row[1,200,72,4],图像行上分为200行,每个行72个grid, 存在4条车道线
loc_col[1,100,81,4],图像列上分为100行,每个行81个grid, 存在4条车道线
顺序分类loss
”To better utilize the prior of the ordinal relationship, we propose to use a base classification loss and an expectation loss.“为了更好的使用有序关系的先验性,使用基分类损失和期望损失。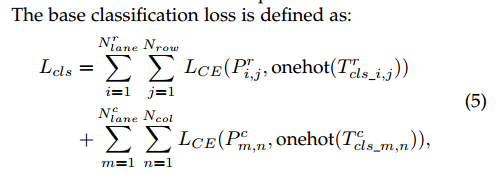
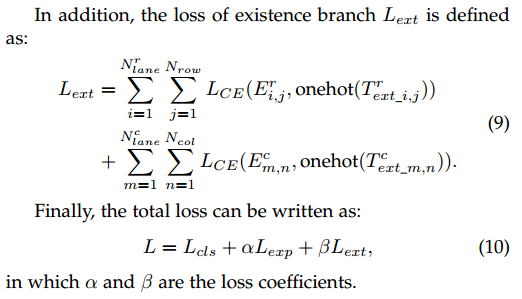
网络模型推理
数据增强
通过简单的数据增强,如调整大小和裁剪,该方法可以快速过拟合整个训练集(接近100%的训练精度,而在测试集上的性能较差)。为了克服过拟合问题,我们提出了一种空间位移数据增强方法,该方法将整个图像和车道标注在空间上随机移动,使网络学习到不同的车道空间模式。由于图像和车道注释的某些部分在空间移位后被裁剪,因此我们扩展了Lane注释直到图像边界。图10为增强效果。